Chapter -11 (Dictionary)
For learn how to download and install python link here: How to download and install python in window
For learn how to run and execute the code in python link here:How to write and run the code
In this blog, the format is first I write Code then Result of that code. You can directly copy the code and so your time save in written that code. Also , image of the code and result and after which it contain explanation of the code.
Example-1: Some important expression
Example-2: Simple dictionary
Code:
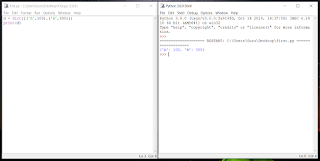
d = {'A':100, 'B':200}
print(d['A'])
Result:
100
Explanation:- Here in 1st line first we create dictionary. Dictionary create in curly bracket and specify the value of name. In this we use A and B.
For example, you go to shop here they return product name and in front of it, its value. The work of dictionary is same.
<Here A and B show the key and 100 and 200 show value.>
Example-3: If use enter dog , cat, mouse then give its definition.
d = {'dog' : 'has a tail and goes woof!',
'cat' : 'says meow',
'mouse' : 'chased by cats'}
Code:
d = {'dog' : 'has a tail and goes woof!',
'cat' : 'says meow',
'mouse' : 'chased by cats'}
word=input('Enter name:')
print('The defination of:', d[word])
Result:
Enter name: cat
The defination is: says meow
Explanation:- It is similar to previous example.
Example-4: To create a dictionary of roman number.
Code:
number= {'I':1, 'V':5, 'X':10, 'L':50 , 'C':100}
print (number['V'])
Result:
5
Explanation:- Similar to example-1
Example-5: Here some name given with their value:
points = {'A':1, 'B':3, 'C':3, 'D':2, 'E':1, 'F':4, 'G':2,'H':4, 'I':1, 'J':8, 'K':5, 'L':1, 'M':3, 'N':1,'O':1, 'P':3, 'Q':10, 'R':1, 'S':1, 'T':1, 'U':1,'V':4, 'W':4, 'X':8, 'Y':4, 'Z':10}
Write a program and user enter 5 times its choice and then add all the score.
Code:
points = {'A':1, 'B':3, 'C':3, 'D':2, 'E':1, 'F':4, 'G':2,
'H':4, 'I':1, 'J':8, 'K':5, 'L':1, 'M':3, 'N':1,
'O':1, 'P':3, 'Q':10, 'R':1, 'S':1, 'T':1, 'U':1,
'V':4, 'W':4, 'X':8, 'Y':4, 'Z':10}
count=0
for i in range(6):
word=input('Enter your choice:')
count=count+points[word]
print('The total score is:',count)
Result:
Enter your choice:Y
The total score is: 4
Enter your choice:F
The total score is: 8
Enter your choice:R
The total score is: 9
Enter your choice:F
The total score is: 13
Enter your choice:C
The total score is: 16
Enter your choice:D
The total score is: 18
Explanation:- First we create dictionary and then by the help of for loop and count we add all the input answer and simply get the result.
Example-6: Represent a deck of card.
Code:
deck = [{'value':i, 'suit':c}
for c in ['spades', 'clubs', 'hearts', 'diamonds']
for i in range(1,14)]
print(deck)
Result:
[{'value': 1, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 2, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 3, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 4, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 5, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 6, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 7, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 8, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 9, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 10, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 11, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 12, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 13, 'suit': 'spades'}, {'value': 1, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 2, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 3, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 4, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 5, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 6, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 7, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 8, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 9, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 10, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 11, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 12, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 13, 'suit': 'clubs'}, {'value': 1, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 2, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 3, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 4, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 5, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 6, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 7, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 8, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 9, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 10, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 11, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 12, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 13, 'suit': 'hearts'}, {'value': 1, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 2, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 3, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 4, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 5, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 6, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 7, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 8, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 9, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 10, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 11, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 12, 'suit': 'diamonds'}, {'value': 13, 'suit': 'diamonds'}]
Explanation:- Here first we use value and card suit then give the range so that it form the complete deck.
Example-7: Copy this dictionary d = {'A':100, 'B':200}
Code:
d = {'A':100, 'B':200}
d2 = d.copy()
print(d2)
Result:
{'A': 100, 'B': 200}
Explanation:- Simply by use of copy command you can copy the dictionary.
Example-8: Write the value of the key and if key not present in dictionary then show not found. Take d = {'A':100, 'B':200}
Code:
d = {'A':100, 'B':200}
letter = input('Enter a letter: ')
if letter in d:
print('The value is', d[letter])
else:
print('Not in dictionary')
Result:
Enter a letter: A
The value is 100
< When you restart the shell>
Enter a letter: J
Not in dictionary
Explanation:- Simply you understand if read previous chapter.
Example-9.1: Write a program and find the key in dictionary.
Code:
d = {'A':100, 'B':200, 'C':100}
L = [x[0] for x in d.items() if x[1]==100]
print(L)
Result:
['A', 'C']
Explanation:- You easily able to understand all thing except why put x[0]. For this see in next example.
Example-9.2: Write a program and find the key in dictionary.
Code:
d = {'A':100, 'B':200, 'C':100}
L = [x[1] for x in d.items() if x[1]==100]
print(L)
Result:
[100,100]
Explanation:- In the previous example you see A , C but here 100 and 100, because '0' denote for key and '1' denote for value.
Example-10: To convert list into dictionary.
Code:
d = dict([('A',100),('B',300)])
print(d)
Result:
{'A': 100, 'B': 300}
Explanation:- By using dict command we able to convert list into dictionary.
Example-11: How to open the text file from the pc. First save the file to your desktop, In my case, I save a file with the name of text in desktop.
Code:
t=open('text.txt').read()
print(t)
Result:
ajshfhgotgho ho osaj opijsdjrop ujiopaj iopejtaioa opajys jaopihjy ojc lhl ghncxog hohj goi hjro rioehjr iozjsol; ejo;jfo;d hjol;j
Explanation:- In the result you see random word these same written in that file , which I save in the desktop of my Pc. You can check own.
Example-12: Open the random file from your pc and then remove all the punctuation from the file. I take the file which is previous save on my desktop as the name of 'text'.
Code:
t=open('text.txt').read()
from string import punctuation
text=t.lower()
for p in punctuation:
text=text.replace(p,'')
words=text.split()
print(words)
Result:
['ajshfhgotgho', 'ho', 'osaj', 'opijsdjrop', 'ujiopaj', 'iopejtaioa', 'opajys', 'jaopihjy', 'ojc', 'lhl', 'ghncxog', 'hohj', 'goi', 'hjro', 'rioehjr', 'iozjsol', 'ejojfod', 'hjolj']
Explanation:- You see these code 'for p in punctuation' in previous chapter, in the next line you see replace so this command help in replace the punctuation from the file.
<If you want to join then use ''.join(words)
Example-13: Give the value to the key in the text file you save on your desktop.
Code:
t=open('text.txt').read()
from string import punctuation
text=t.lower()
for p in punctuation:
text=text.replace(p,'')
words=text.split()
d = {}
for w in words:
if w in d:
d[w] = d[w] + 1
else:
d[w] = 1
print(d)
Result:
{'ajshfhgotgho': 1, 'ho': 1, 'osaj': 1, 'opijsdjrop': 1, 'ujiopaj': 1, 'iopejtaioa': 1, 'opajys': 1, 'jaopihjy': 1, 'ojc': 1, 'lhl': 1, 'ghncxog': 1, 'hohj': 1, 'goi': 1, 'hjro': 1, 'rioehjr': 1, 'iozjsol': 1, 'ejojfod': 1, 'hjolj': 1}
Explanation:- Here you see command like previous example but few more code which is used to give the value to the key. Here all value are 1 beacuse use else: d[w]=1 ,and if you put here 2 then all value are 2.
Example-14: Arrange all the key in alphabetical order take the file that you save on you desktop as the name of text.
Code:
t=open('text.txt').read()
from string import punctuation
text=t.lower()
for p in punctuation:
text=text.replace(p,'')
words=text.split()
d = {}
for w in words:
if w in d:
d[w] = d[w] + 1
else:
d[w] = 1
items = list(d.items())
items.sort()
for i in items:
print(i)
Result:
('ajshfhgotgho', 1)
('ejojfod', 1)
('ghncxog', 1)
('goi', 1)
('hjolj', 1)
('hjro', 1)
('ho', 1)
('hohj', 1)
('iopejtaioa', 1)
('iozjsol', 1)
('jaopihjy', 1)
('lhl', 1)
('ojc', 1)
('opajys', 1)
('opijsdjrop', 1)
('osaj', 1)
('rioehjr', 1)
('ujiopaj', 1)
Explanation:- Here we first convert into list by using d.items(). Then use sort command which arrange all the key in the alphabetical order. You read sort command in chapter-7 (list).
Example-15: Write a program and print first the value of the dictionary then the key arrange in alphabetical order. Take example the same file which you save on your desktop.
Code:
t=open('text.txt').read()
from string import punctuation
text=t.lower()
for p in punctuation:
text=text.replace(p,'')
words=text.split()
d = {}
for w in words:
if w in d:
d[w] = d[w] + 1
else:
d[w] = 1
items = list(d.items())
items = [(i[1], i[0]) for i in items]
items.sort()
for i in items:
print(i)
Result:
(1, 'ajshfhgotgho')
(1, 'ejojfod')
(1, 'ghncxog')
(1, 'goi')
(1, 'hjolj')
(1, 'hjro')
(1, 'ho')
(1, 'hohj')
(1, 'iopejtaioa')
(1, 'iozjsol')
(1, 'jaopihjy')
(1, 'lhl')
(1, 'ojc')
(1, 'opajys')
(1, 'opijsdjrop')
(1, 'osaj')
(1, 'rioehjr')
(1, 'ujiopaj')



















No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt, let me know.